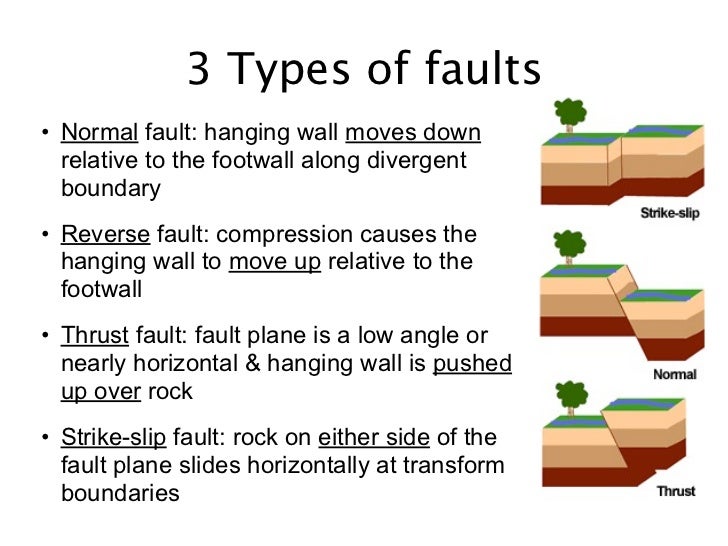
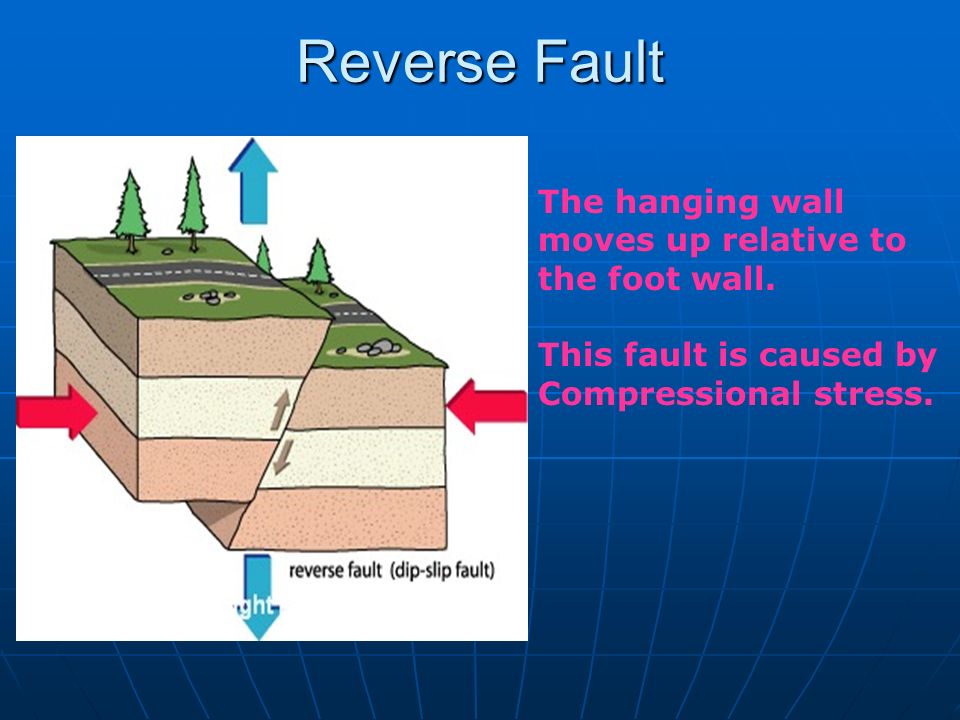
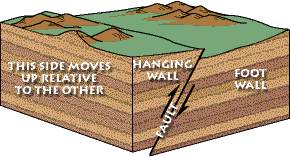
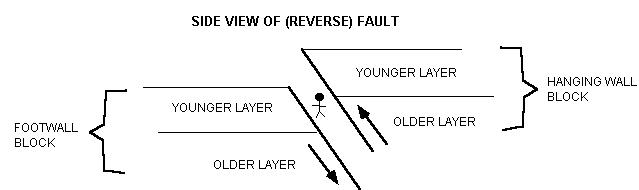
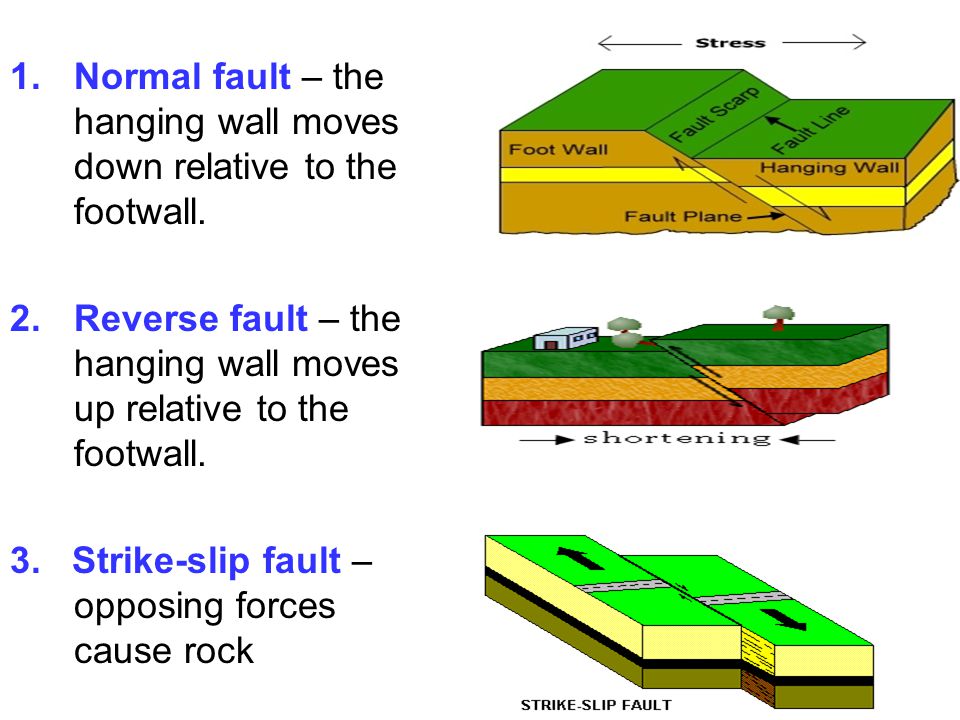
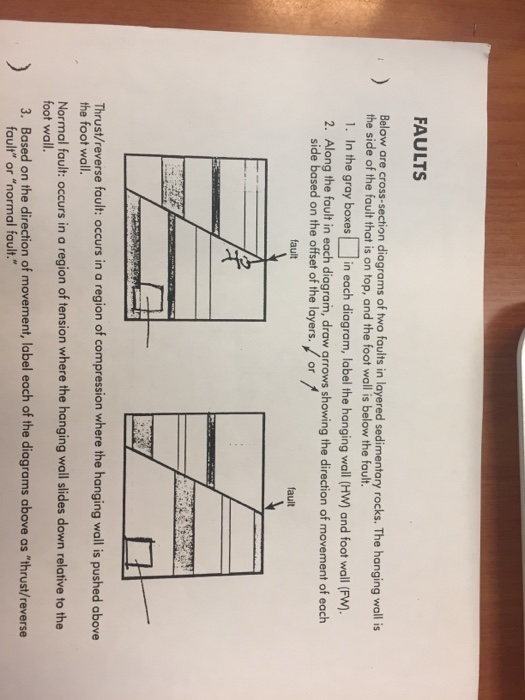
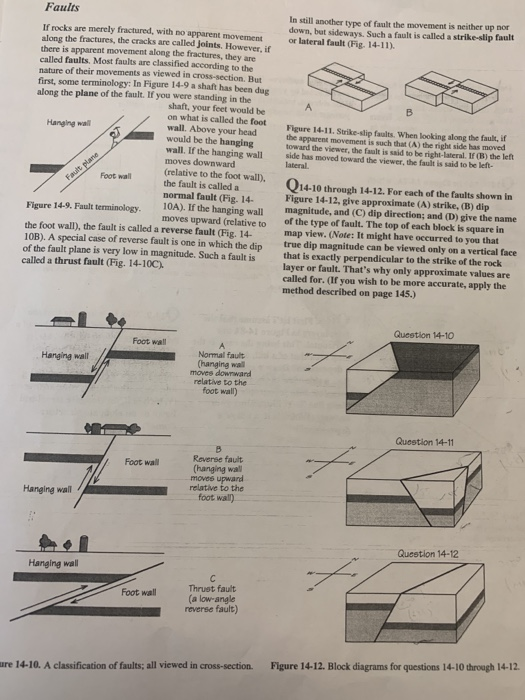
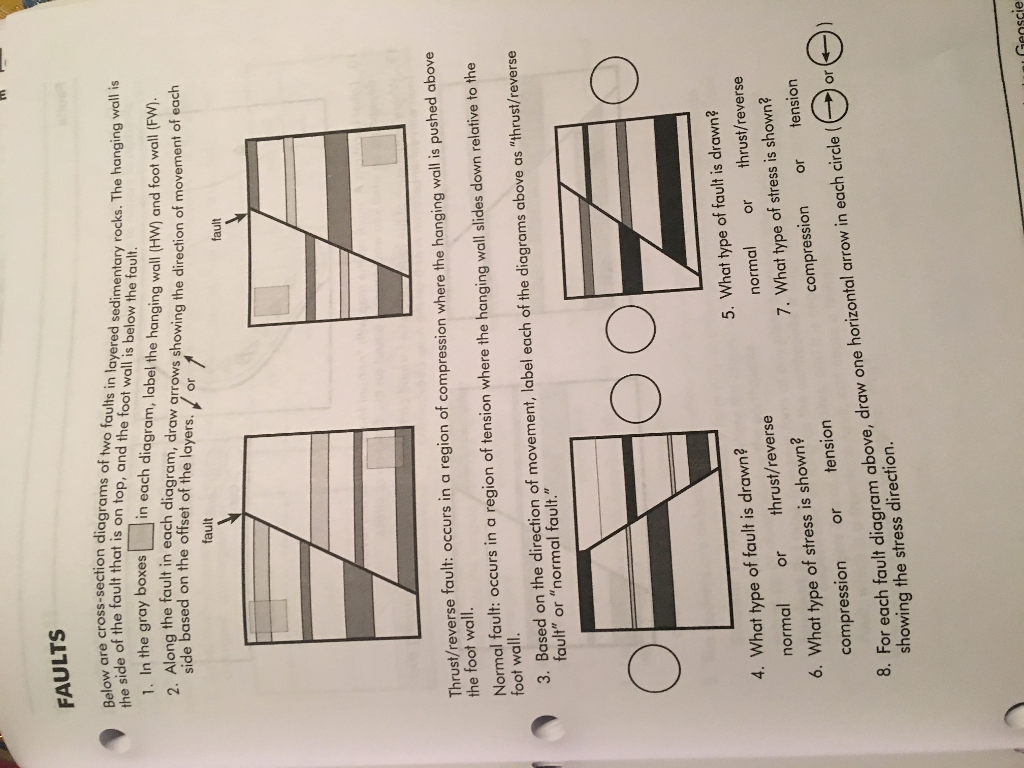
In a reverse fault the hanging wall moves upward relative to the foot wall.
In a reverse fault where does the hanging wall move relative to the footwall.
What types of faults would you.
True the oldest sedimentary rock strata are exposed along the axial parts of deeply eroded anticlines.
In a reverse fault the hanging wall moves down and the footwall moves up.
In a normal fault the hanging wall of the fault moves down relative to the foot wall.
A reverse fault is in a zone of compressional faulting rocks in the hanging wall are pushed up relative to rocks in the footwall.
Alternatively such a fault can be called an extensional fault.
Mike dunning dorling kindersle getty images reverse faults form when the hanging wall moves up.
A normal fault is in a zone of tensional faulting rocks in the.
Another type of fault is the thrust fault where ground on one side of the fault moves up and over adjacent ground.
In a normal fault the hanging wall of the fault moves down relative to the foot wall.
A normal fault occurs when the crust is extended.
A reverse fault is in a zone of compressional faulting rocks in the hanging wall are pushed up relative to rocks in the footwall.
The hanging wall moves downward relative to the footwall.
A normal fault is in a zone of tensional faulting rocks in the.