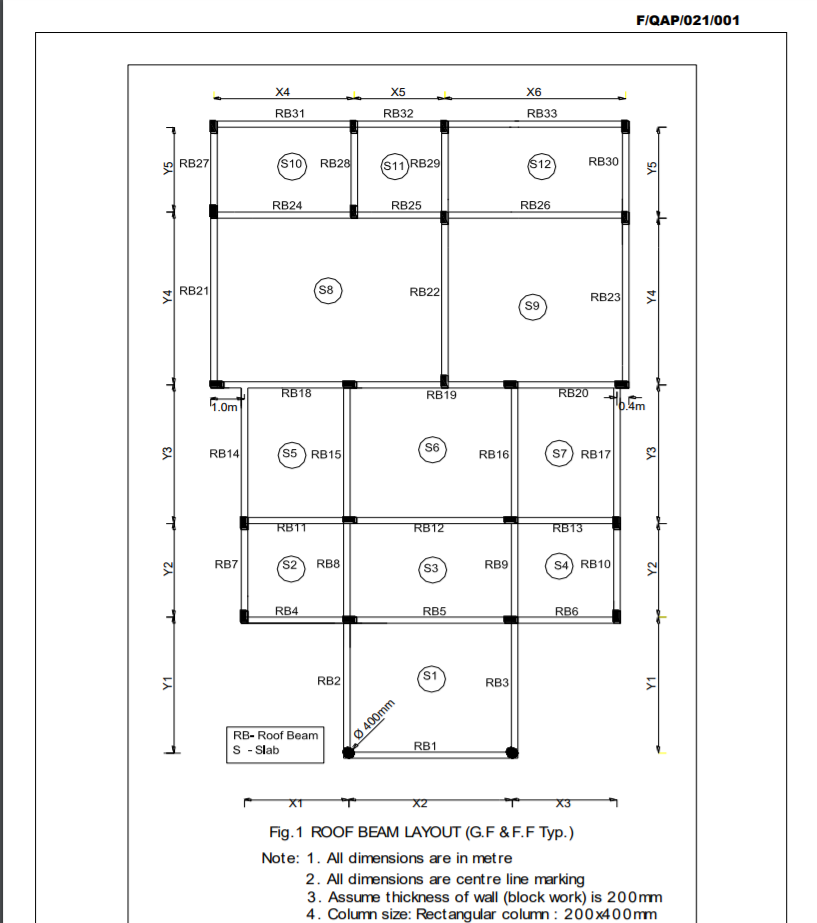
When the imposed load is considered as an accompanying action in accordance with en 1990 only one of the two factors ψ en 1990 table a1 1 and αn 6 3 1 2 11 shall be applied.
Imposed load on roof eurocode.
In eurocode phraseology it is described as a quasi permanent variable action.
Floor and roof areas in buildings are sub divided into 11 categories according to use.
These will be covered in a forthcoming note p this article was updated in october.
If the imposed load is considered as an accompanying action i e.
Actions on structures.
A ψ factor is applied to the imposed load case in a combination then as stated in the base eurocode cl 3 3 2 the imposed load reduction should not be applied at the same time.
Imposed load is defined as the load that is applied to the structure that is not permanent and can be variable.
Reductions can not however be applied to roof imposed loads.
Roofs do not qualify for load reductions.
6 3 1 2 10 a reduction factor for imposed loads for area aa may be used and should be determined using aa 1 0 a 1000 0 75 na 1 bs en 1991 1 1.
En 1991 1 1 imposed loads 6 2 1 floors beams and roofs 1 p for the design of a floor structure within one storey or a roof the imposed load shall be taken into account as a free action applied at the most unfavourable part of the influence area of the action effects considered.
The method given below complies with the bs en 1991 1 1 uk national annex but differs from that given the eurocode.
Loads specified are represented by uniformly distributed loads udl concentrated loads line loads.